System Modeler Library Store
The HighSchoolBiology library contains interactive biology labs for high-school students. After completing the labs, you will be able to understand how osmosis works in the movement of water in and out of a red blood cell (RBC), why epidemiology is important in creating a healthy society, and how the food you consume affects the body. The library also contains many exercises related to cell transport phenomena, population models and food metabolism.
Features
Examples
Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane not only acts as a cell barrier, but also controls what comes into and out of a cell. In this virtual lab, you will explore the concept of osmosis and how molar concentrations of solutes affect the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane.
Model
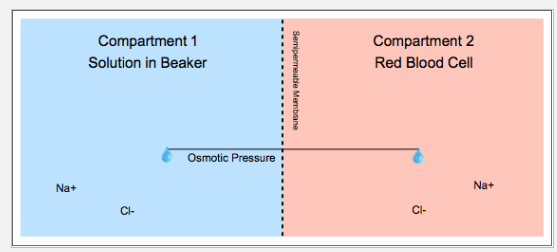
The models contain two compartments. Compartment 1 represents the solution in the beaker, while compartment 2 represents the contents of the RBC. A semipermeable membrane separates these two compartments and only allows water to pass between them.
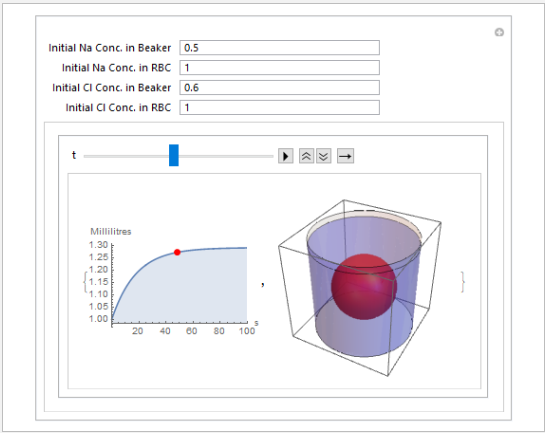
Analysis
When there is a difference in the concentration of solutes on either side of the membrane, pressure builds up at the membrane surface. Water then moves across the membrane from the compartment with the low solute concentration to the compartment with the high solute concentration.
Ibuprofen
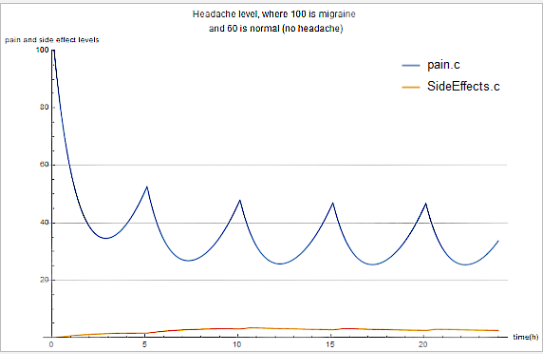
Most people have had headaches that prevent them from focusing on their tasks. In this virtual lab, you will study how ibuprofen can relieve headaches. Your goal is to find out what dosage works best to relieve the headache without getting any side effects.
Model
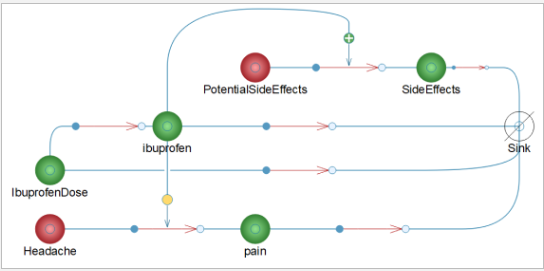
Use built-in components to model the pain during headaches, ibuprofen and potential side effects.
Analysis
As long as the side effect signal is kept below 20, there will be no significant side effects. You will have no sensation of headache if the headache signal is kept below 60 and above 40.
Food Metabolism
How does the food you consume affect your body, and what type of food should you consume to build muscle? Most people have thought about this question at least once. In this virtual lab, you will explore how your chosen food options contribute toward fat and muscle gain.
Model
The body is a complex system. The model used in this lab is a very simplified version of this complex reality. Food intake gets divided into protein, carbohydrates and fat. These then get converted into muscle and fat mass, depending upon various factors, such as metabolic rate, physical activity and so on.
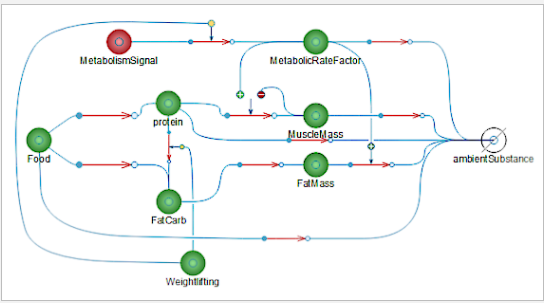
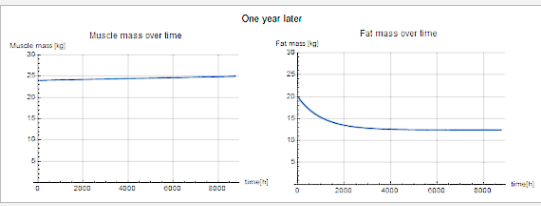
Analysis
Analyze the development of fat and muscle mass for a given diet.
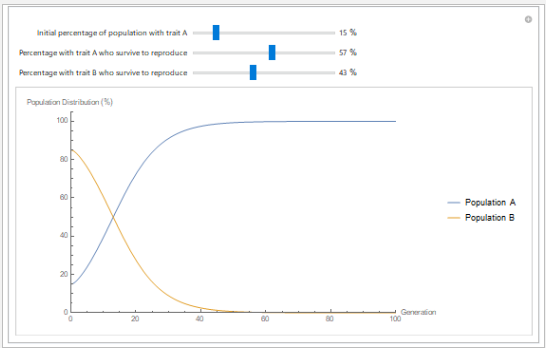
Natural Selection
Natural selection is fundamental in understanding how populations evolve over time. It helps with understanding why some traits die out while others flourish. In this virtual lab, you will explore the effect that environmental selection pressures have on the genetic makeup of a population.
Model
The scenarios you will explore in this virtual lab consist of different population groups with transitions, denoted by arrows, between them. The rate of transition can be modified by the number of individuals in a population; for example, a high number of individuals from population A will promote new individuals being born into the population group.
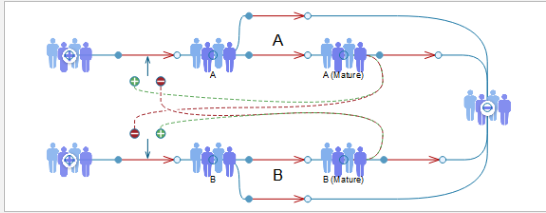
Analysis
If a group of organisms with a particular trait has a decreased chance of surviving to reproduce, there is a decreased chance that the genes for this trait will be passed on to the next generation. This in turn may lead to the extinction of the trait.
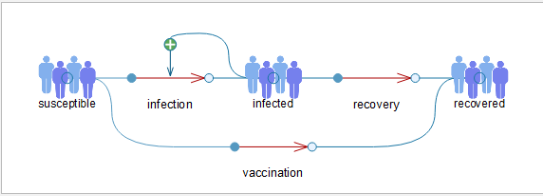
Herd Immunity
When a large percentage of the population becomes immune to a disease such as COVID-19, you can consider the population to be protected from the disease by herd immunity. This means that although 100% of the population may not be vaccinated, a sufficient proportion of the population is, and the rate of infection starts to decrease. In this virtual lab, you will investigate the concept of herd immunity using the SIR (susceptible, infected and recovered) model.
Model
The model used in this exercise is based on the SIR (susceptible, infected, recovered) model. This classical epidemiological model was developed by Kermack and McKendrick in the early 1900s and is one of the most well-known models for studying infectious diseases within populations. Since its development, there have been many adaptations of the model, allowing it to be used in a wide variety of settings and contexts.
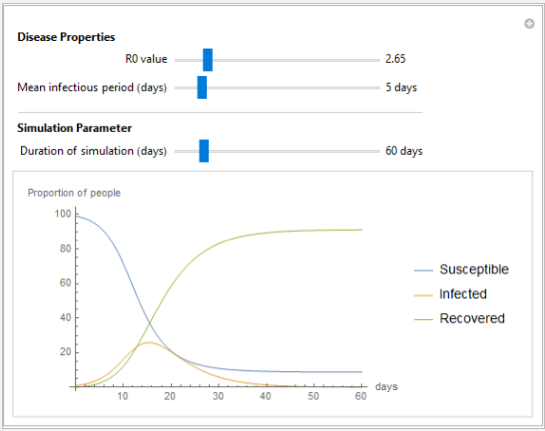
Analysis
Analyze the impact of infection for different basic reproduction number (R0) values and mean infectious period. To model the influence of COVID-19, set the R0 value to 2.65 and the mean infectious period to 5 days.
Details
|
Version |
1.1 |
Platforms |
All Platforms |
|
Updated |
April 2020 |
Requirements |
None |
|
Size |
<15MB |
Language |
English |
|
Library Dependency |
Modelica Standard Library 3.2.3 |
Support |
support@wolfram.com |
|
SystemModeler Compatibility |
12.0 and higher |
Documentation |
Self documenting |
|
Mathematica Compatibility |
12.0 and higher |
License
|
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0
|
© Copyright 2000-2025 COGITO SOFTWARE CO.,LTD. All rights reserved